Welcome to our article on melasma! In this article, we take a closer look at what exactly melasma is and how you can treat this common skin condition. Whether you have melasma yourself or just want to learn more about this condition, we've got all the information you need.
What is melasma?
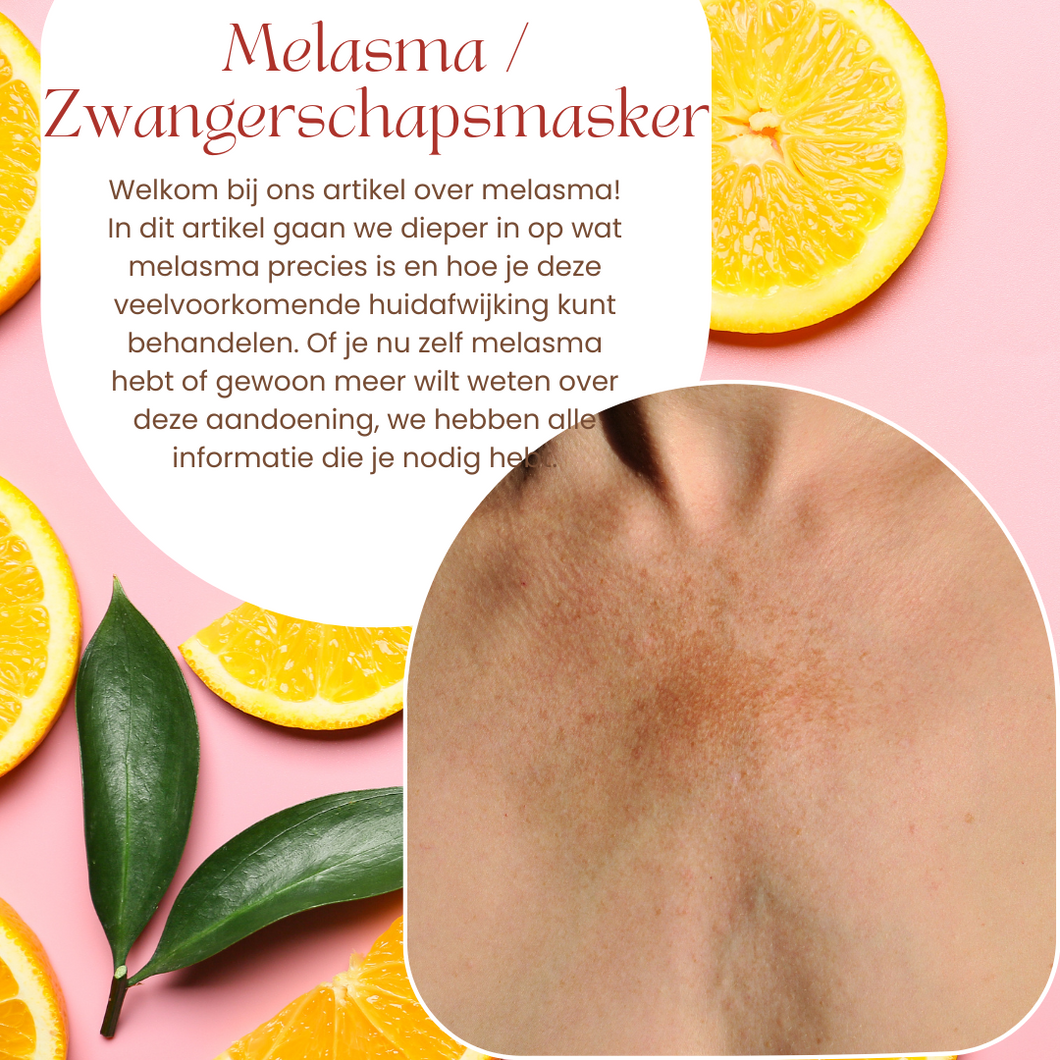
Melasma is a common skin condition in which dark spots appear on the skin. These spots mainly appear on the face and are often associated with pregnancy, hormonal changes and sun exposure. Melasma is also known as pregnancy mask because it often occurs in pregnant women.
How Does Melasma Occur?
Melasma occurs when the pigment cells in the skin become overactive and produce too much pigment. This can be caused by hormonal fluctuations, such as during pregnancy or when using birth control pills. In addition, sun exposure can also contribute to the development of melasma.
How can you treat melasma?
There are several treatments available for melasma, depending on the severity of the condition. Some treatments that can be used are:
- Creams and ointments: There are several creams and ointments available that can help to reduce the dark spots. These creams often work by inhibiting pigment production in the skin.
- Chemical peels: In a chemical peel, an acid is applied to the skin, causing the top layer of the skin to flake off. This can help reduce the dark spots.
- Laser therapy: Laser therapy uses light to destroy the pigment cells in the skin. This can be an effective treatment for melasma.
It is important to know that melasma is a chronic condition and the dark spots can often come back even after successful treatment.
FAQs
- Is melasma dangerous?
- No, melasma is not dangerous. It can be cosmetically disturbing.
- Can melasma go away on its own?
- Melasma may go away on its own, but it usually doesn't.
- Is melasma contagious?
- No, melasma is not contagious.
- Can you prevent melasma?
- Preventing melasma is tricky, but wearing sunscreen can help reduce the development of melasma.
- Is melasma the same as age spots?
- No, melasma is not the same as age spots. Melasma is caused by hormonal fluctuations and sun exposure, while age spots are caused by skin aging.
Melasma is one common skin condition in which dark spots appear on the skin. These spots are often cosmetically disturbing, but fortunately there are several treatments available to reduce them. It is important to know that melasma is a chronic condition and the spots can often come back.
How long do the results of a melasma treatment last?
The results of a melasma treatment are generally long-lasting, but the dark spots can unfortunately come back. It is therefore important to continue to protect the skin against the sun.
Melasma: Ascorbic Acid vs. Hydroquinone
Melasma is a common skin condition that causes brown patches on the face, usually on the cheeks, forehead, nose and upper lip. While not harmful, it can be frustrating to deal with and can have a significant impact on one's self-confidence.
There are several treatments available for melasma, but two of the most popular options are ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and hydroquinone. In this article, we will discuss these two treatments in detail, comparing and contrasting their effectiveness, safety, and possible side effects.
What is Melasma?
Before discussing the treatments, it's important to understand what melasma is and what causes it. Melasma is a skin condition characterized by dark, brown or gray-brown spots on the face. It mainly affects women and people with darker skin tones, but it can also occur in men and people with lighter skin tones.
The exact cause of melasma is not known, but it is associated with a number of factors, including hormones, sunlight, and genetics. Women who are pregnant or using hormonal birth control have an increased risk of melasma because hormonal fluctuations can affect pigment production in the skin.
Ascorbic acid
Ascorbic acid, more commonly known as vitamin C, is a powerful antioxidant known for its many health benefits. It is often used in skin care products for its ability to protect the skin from free radical damage and stimulate collagen production.
When it comes to treating melasma, ascorbic acid is often used for its ability to brighten the skin and reduce dark spots. It works by inhibiting the production of melanin in the skin, reducing pigmentation.
Ascorbic acid is usually used in the form of a serum or cream that is applied directly to the skin. It may take several weeks to months to see results, depending on the severity of the melasma.
Hydrochinon
Hydroquinone is a powerful whitening agent often used in skin care products to reduce dark spots and pigmentation. It works by inhibiting the production of melanin in the skin and breaking down the existing melanin, thereby brightening the skin.
While hydroquinone can be very effective in treating melasma, it also has a number of possible side effects. Bee
prolonged use can irritate and discolor the skin, possibly making the problem worse. Therefore, it is usually only prescribed for short-term use and under the close supervision of a dermatologist.
In addition, hydroquinone is banned or prescription-only in some countries due to its potential health risks. For example, it is banned in the European Union and Japan due to its potential carcinogenic effects.
Ascorbic Acid vs Hydroquinone: Which One Is Better?
While both ascorbic acid and hydroquinone can be effective in treating melasma, there are some key differences between the two. Here are some factors to consider when choosing between these treatments:
effectiveness
Both treatments can help reduce melasma, but some studies suggest that hydroquinone may be more effective than ascorbic acid. A 2013 study published in the Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery compared the effectiveness of hydroquinone and ascorbic acid in treating melasma and found that hydroquinone caused significantly better skin lightening than ascorbic acid.
Safety
While both treatments are generally considered safe, hydroquinone has more potential side effects than ascorbic acid. With prolonged use, it can irritate and discolor the skin, and in rare cases can lead to serious health problems. Ascorbic acid, on the other hand, has little to no side effects and is generally well tolerated.
Cost
Hydroquinone is generally more expensive than ascorbic acid, especially when prescribed by prescription. In addition, it may be necessary to undergo multiple treatments to achieve the desired results, which can further increase costs.
Availability
Hydroquinone is banned or prescription-only in some countries due to its potential health risks, while ascorbic acid is generally readily available over the counter. If you live in a country where hydroquinone is not available, ascorbic acid may be a good option.
If you are looking for an effective treatment for melasma, both ascorbic acid and hydroquinone are worth considering. While hydroquinone may be potentially more effective, it also has more side effects and may be more expensive. Ascorbic acid has few side effects, is generally readily available, and can be effective in reducing melasma.
Frequently Asked Questions About Melasma Treatments
Here are some frequently asked questions about melasma treatments:
1. Is Ascorbic Acid Safe For Skin?
Yes, ascorbic acid is generally safe for the skin and has little to no side effects. However, it is important to do a patch test before using a new skincare product to avoid allergic reactions.
2. How long does it take to see results with ascorbic acid?
It may take several weeks to months to see results with ascorbic acid, depending on the severity of your melasma and how consistently you use the treatment.
3. Is hydroquinone safe for long-term use?
No, hydroquinone can irritate and discolor the skin with prolonged use, and it also carries an increased risk of health problems. Therefore, it is usually only prescribed for short-term use and under the close supervision of a dermatologist.
4. Can I use ascorbic acid and hydroquinone at the same time?
Yes, it is possible to use ascorbic acid and hydroquinone at the same time, but this should always be done under the supervision of a dermatologist to avoid possible side effects.
5. What else can I do to reduce melasma?
In addition to ascorbic acid and hydroquinone, other treatments are available for melasma, including retinoids, azelaic acid, and laser therapy. It is also important to protect your skin from the sun by using sunscreen and covering your face with a hat or umbrella.
Concluding thoughts
Melasma can be a frustrating condition to deal with, but several treatments are available to help ease the symptoms. Ascorbic acid and hydroquinone are two of the most popular options, and while they differ in effectiveness, safety, and cost, they can both help reduce melasma. Always consult a dermatologist before trying any new treatment, and follow their recommendations for best results.